National Hurricane Center’s Monitoring and Tracking of Beryl

National hurricane center beryl – The National Hurricane Center (NHC) plays a crucial role in monitoring and tracking hurricanes, including Beryl. The NHC is responsible for issuing hurricane advisories and watches, providing critical information to coastal communities and emergency managers.
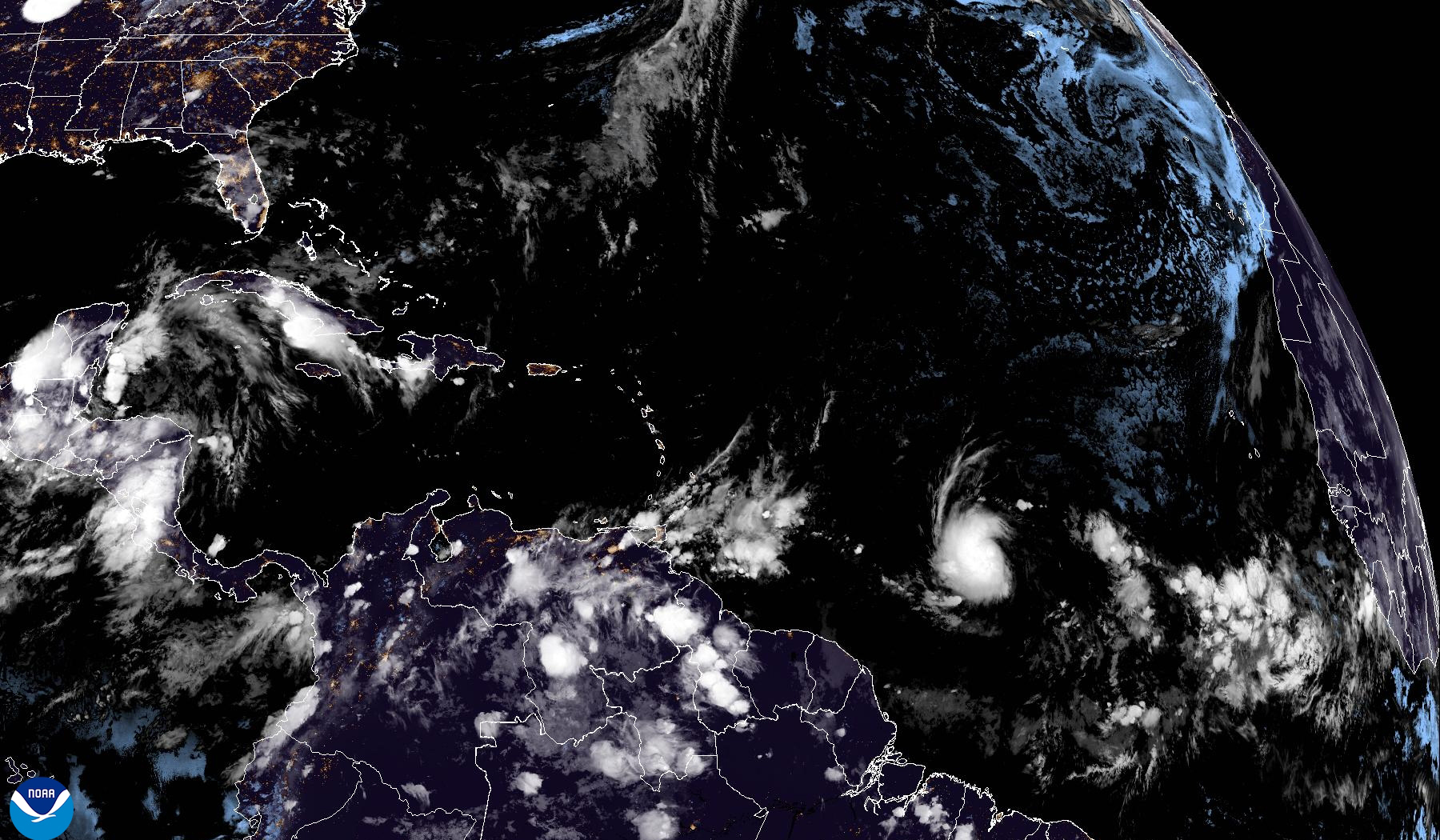
The NHC uses a variety of tools and technologies to track and predict hurricane movement. These include satellite imagery, radar data, and computer models. The NHC also has a team of meteorologists who analyze the data and provide forecasts.
National Hurricane Center Beryl is currently tracking a tropical storm in the Atlantic Ocean. Forecasters are using spaghetti models for beryl to predict its potential path. Spaghetti models for beryl are computer simulations that show the possible paths a storm could take.
The National Hurricane Center Beryl will continue to monitor the storm and provide updates as needed.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery is one of the most important tools used by the NHC to track hurricanes. Satellites can provide images of hurricanes from space, which can help meteorologists determine the storm’s size, shape, and intensity.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is closely monitoring Tropical Storm Beryl. For the latest updates on its track and intensity, visit the NHC website. To visualize potential paths of the storm, explore interactive hurricane beryl spaghetti models. The NHC will continue to provide regular updates as the storm progresses.
Radar Data, National hurricane center beryl
Radar data can be used to track the movement of hurricanes and to measure their rainfall rates. Radar data can also be used to identify areas of heavy precipitation, which can be helpful for forecasting flooding.
Computer Models
Computer models are used to predict the future movement and intensity of hurricanes. These models use a variety of data, including satellite imagery, radar data, and historical hurricane data, to make their predictions.
Historical and Climatological Context of Beryl: National Hurricane Center Beryl
Tropical cyclones have a long and destructive history in the region affected by Beryl. In the past century, several major hurricanes have made landfall in this area, causing widespread damage and loss of life. Some of the most notable hurricanes to impact the region include the Great Galveston Hurricane of 1900, Hurricane Camille in 1969, and Hurricane Katrina in 2005.
The climatological factors that influence hurricane formation and movement in the area include:
- Warm ocean temperatures: The warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean provide the energy that fuels hurricanes.
- Favorable wind patterns: The prevailing winds in the region help to steer hurricanes towards the coast.
- Low vertical wind shear: Low vertical wind shear allows hurricanes to maintain their organization and intensity.
Beryl shares some similarities with other notable hurricanes that have impacted the region. Like Hurricane Katrina, Beryl is a Category 4 hurricane that is expected to make landfall along the Gulf Coast. However, Beryl is also expected to be a smaller and faster-moving storm than Katrina. This means that it may cause less widespread damage, but it could still be a dangerous storm for coastal communities.
Potential Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for Beryl
Hurricane Beryl poses potential impacts to affected areas, including storm surge, flooding, and wind damage. Understanding these impacts and implementing mitigation strategies are crucial for reducing risks and safeguarding lives and property.
Storm Surge
Storm surge is a dangerous rise in sea level caused by a hurricane’s winds and pressure. Beryl’s storm surge can lead to flooding in coastal areas, damaging homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
- Stay informed about storm surge forecasts and evacuation orders.
- Move to higher ground or inland areas before the storm surge arrives.
- Secure loose objects outside your home that could be carried away by floodwaters.
Flooding
Heavy rainfall from Beryl can cause significant flooding, leading to road closures, property damage, and hazardous conditions.
- Monitor weather forecasts and be aware of flood warnings.
- Avoid driving through flooded areas.
- Elevate belongings and furniture to higher levels to prevent water damage.
Wind Damage
Beryl’s strong winds can cause structural damage to buildings, down power lines, and uproot trees. Wind damage can pose risks to life and property.
- Secure loose items outside your home, such as patio furniture and grills.
- Reinforce windows and doors with shutters or plywood.
- Have a plan for where you will go if you lose power or need to evacuate.
Preparedness Measures
Individuals and communities in affected areas should take the following preparedness measures:
- Develop an emergency plan and share it with family and friends.
- Stock up on non-perishable food, water, and essential supplies.
- Secure important documents and valuables.
- Stay informed about weather forecasts and follow instructions from local authorities.